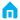
- instrument cable type selection specification
According to the project contract, the standards to be followed are determined. At present, the cable modeling standards are mainly EN56288-7 and UL2250
- instrument signal cable structure
- Conductor: ul2250 annealed copper conductor, conductor should be continuous, in accordance with ASTMB3 regulations
- . Stranded wire core is recommended for EN50288-7 and ul2250. At this time, the distributed capacitance and distributed inductance are very close to each other. The interference potentials caused by coupling cancel each other, which can effectively suppress electromagnetic interference, and can also suppress electrostatic interference to a certain extent.
- EN-50288-7. The ul2250 has certain requirements on the cable twisted pitch. Joint pitch is the distance traveled by one rotation along the axis of the strand, It has to do with the cross section of the conductor EN-50288-7 stipulates that the hinge pitch shall not exceed 100mm when the conductor section is less than 1.5mm². When the conductor section is 2.5mm², the pitch shall not exceed 150mm. ul2250 states:
2-core cable stranding pitch does not exceed 30 times the core diameter. (See table below)
3 core 35 times
4 core 40 times
≥ 5 core cable 55 times
The ratio of stranded pitch to conductor diameter can be defined as the pitch ratio.
The pitch ratio is large, the stranding is not close, and the use process is easy to loose strands, the pitch ratio is small, the strand is soft, the stranding is close, but the unit mass of the strand is increased, the material consumption is large, the cable conductivity is reduced.

2.4Insulating layer
EN50288-7 gives five insulating materials: PVC, PE ,PP, Halogen-free flame retardant compounds, xlpe. In cases where cables require a higher temperature rating, appropriate alternative materials may need to be considered. Core area and insulation thickness will affect the working capacitance and impedance characteristics of the cable. EN50288-7 gives the minimum thickness of insulation layer at any point corresponding to different conductor sizes, as shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Minimum insulation thickness corresponding to core area (mm)
| Section Area mm² |
Rated Voltage/V
90 300 500
|
| 0.5 |
0.2 0.26 0.44 |
| 0.75 |
0.2 0.26 0.44 |
| 1.0 |
0.26 0.26 0.44 |
| 1.5 |
0.30 0.35 0.44 |
| 2.5 |
0.55 |
Ul2250 provides more than 20 kinds of insulation materials. The common materials and their corresponding temperatures are listed in Table 2.
Ul2250 also gives the minimum thickness of insulating layer corresponding to several insulating materials in Table 2 under different specifications. See Table 3
Table 2 Temperature grades of insulation materials ° C (℉)
| Mtearial |
Insulation Temp Rating |
| HDPE |
75(167) |
| LDPE |
75(167) |
| PP |
75(167) |
| Reinforced PP |
60(140) |
| PVC |
105(221) |
| 90(194) |
| 75(167) |
| 60(140) |
| Silicone |
200(392) |
| 150(302) |
| XLPE |
105(221) |
| XL-PVC |
90(194) |
| 75(167) |
Table 3. Minimum insulation Thickness corresponding to core specification (mm)
| AWG |
Min Avg Thickness |
Min Thickness AnyPoint |
| 22-20 |
0.3 |
0.28 |
| 19-15 |
0.38 |
0.38 |
| 14-12 |
0.51 |
0.46 |
The minimum thickness of the cable insulation layer is the basis to ensure the reliable operation of the cable under the action of overvoltage

2.5 Shielding Layer
When a conductor is in a changing magnetic field, the signal loop is prone to electromagnetic interference and electrostatic induction interference, plus the loop signal is generally 4-20MA or 1-5V weak signal, belongs to the low level range, the signal may be interfered and distorted. In order to ensure the accuracy, sensitivity and reliability of the entire control loop, the cable needs a shield layer to improve its resistance.
In general, switching signals should be used with OVERALL shielding. Overall shielding is recommended for 4-20MA or 1-5v signals. Individual shielding and overall shielding should be used for thermocouple or pulse signal. Individual shielding and Overall shielding should be used for signal cables.
EN5288-7 provides three shielding methods: 1. The minimum coverage of common or plated braided shielding shall be 60% 2. Foil and COPPER OR PLATED COPPER braided shield. Add drainage wire, drainage wire should be solid or stranded, the material of bare copper or plated copper, such as TC 3. A minimum of 20% of the foil area is required to overlap, and the drain is always connected to the metal surface of the foil.
UL2250 also provides three shielding methods: 1. Metal-polyester shielding tape. The drainage cable must be bare copper and connected to the metal side. If the metal is aluminum, the drainage cable needs to be plated with other metals. 2. Bare copper wire or plated copper wire braid. 3. Bare copper tape or metal-plated tape.
The above specification does not specify which material and form of shielding layer should be selected, which should be specified by the customer or negotiated between the customer and the manufacturer according to the project contract.
2.6 Armored layer.
The cable is easy to be compressed or scratched in the laying or use process, and the armored layer can effectively reduce the mechanical damage.
1. EN50288-7 provides three types of armor. One layer of round or flat galvanized steel wire and two layers of steel or copper tape. Braided armor of galvanized steel or tinned copper.
2. Ul2250 is also given in several forms of armor. Smooth metal sheathed, welded corrugated metal sheathed, extruded corrugated metal sheathed, link sheathed.
3. Whether the cable is armored depends on the project requirements. If the cable has been protected in the bridge or casing, it can not be armored.

2.7 Sheath
Because the application of instrument cables may be high temperature, low temperature, high radiation or wet environment, so the cable jacket should be flame retardant, resistance to UV, oil, moisture and other functions.
EN50288-7 requires that the outer sheath material should be suitable for operating temperature, which can be the following. PVC meets EN5020-22 and PE meets EN50290-2-24. Halogen-free flame retardant material conforms to EN50290-2-27. The thickness of the outer sheath should be uniform. The thickness depends on the outer diameter of the cable. When there is no armored layer, the thickness of the outer sheath SRT=0.028D+1-1(MM),D is the cable diameter, the minimum thickness at any point should not be less than (normal thickness * 15% +0.1) mm minimum average thickness should not be less than the normal thickness. When armored layer, the thickness of the outer sheath SRt=0.04D+0.7 (mm) The minimum thickness at any point should not be less than (normal thickness * 20% +0.2) mm
Ul2250 provides more than 20 sheathing materials and corresponding temperature grades.
Several common materials can be listed in Table 6
Table 6 Cable sheathing materials and corresponding temperature grades ℃ (℉
| Mtearial |
Insulation Temp Rating |
| PVC |
105(221)) |
| |
90(194) |
| |
75(167) |
| |
60(140) |
| Silicone |
200(392) |
| |
150(221) |
| xl-pvc |
90(194) |
| |
75(167) |
If the temperature of the insulation layer is 60-105 ° C, the temperature of the sheathing material should not be more than 15 ° C lower than that of the insulation layer. The cable temperature rating is equal to the insulation layer temperature rating. If the cable insulation temperature rating is 125-250℃, the relationship between the sheath temperature rating and the insulation temperature rating is not clear, but the cable temperature rating should be the minimum between the sheath temperature rating and the insulation temperature rating.
Ul2250 also provides the minimum sheathing thickness corresponding to several sheathing materials in Table 6 under different conductor sizes. As shown in Table 7, the minimum cable sheath thickness at any point should not be less than 80% of the average thickness of the minimum sheath
When the cable is armored, the armored layer must have an outer sheath. In other cases, the outer sheath is not included. If the outer sheath is fluoropolymer, the thickness of the sheath is as shown in Table 7. If it's a fluoropolymer jacket. Sheath thickness shall meet the requirements listed in Table 8.
Table 7 The corresponding relationship between the minimum thickness of the cable sheath and the cable sheath
| O.D. |
Min Thickness of sheath |
Min Thickness AnyPoint |
| ≤5.08 |
0.89 |
0.71 |
| >5.08且≤7.62 |
1.02 |
0.81 |
| >7.62且≤12.07 |
1.27 |
1.02 |
| >12.07且≤19.05 |
1.52 |
1.22 |
| >19.05且≤27.94 |
1.77 |
1.41 |
| >27.94且≤36.83 |
2.03 |
1.63 |
| >36.83且≤45.72 |
2.29 |
1.83 |

Table 8 Correspondence between the minimum thickness of armored cable outer sheath and the lower diameter of sheath (mm)
| O.D. |
Min Thickness of sheath |
Min Thickness AnyPoint |
| ≤5.08 |
0.89 |
0.76 |
| >5.08且≤10.80 |
1.02 |
0.81 |
| >1.08且≤38.10 |
1.27 |
0.89 |
| >38.10且≤57.15 |
1.52 |
1.32 |
| >57.15且≤76.20 |
1.90 |
1.07 |
| >76.2 |
2.16 |
1.52 |
More products 1
More products 2
More products 3

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!